在之前的一篇文章《IoC概述及Spring中的IoC》中已经介绍了Spring IoC容器的相关概念,本文将通过一个具体案例来介绍如何使用XML配置的方式来使用Spring的IoC容器。
一、前期准备
假设有一个账户管理系统,该系统包含了服务层和数据访问层,现在需要使用Spring框架来降低模块之间的耦合度,那么该如何实现这个要求呢?
1、创建工程
新建一个Maven工程,并编写服务层接口和实现类以及数据访问层的接口和实现类,代码如下:
(1)数据访问层接口IAccountDao
1 | package cn.frankfang.dao; |
(2)数据访问层实现类AccountDaoImpl
1 | package cn.frankfang.dao.impl; |
(3)服务层接口IAccountService
1 | package cn.frankfang.service; |
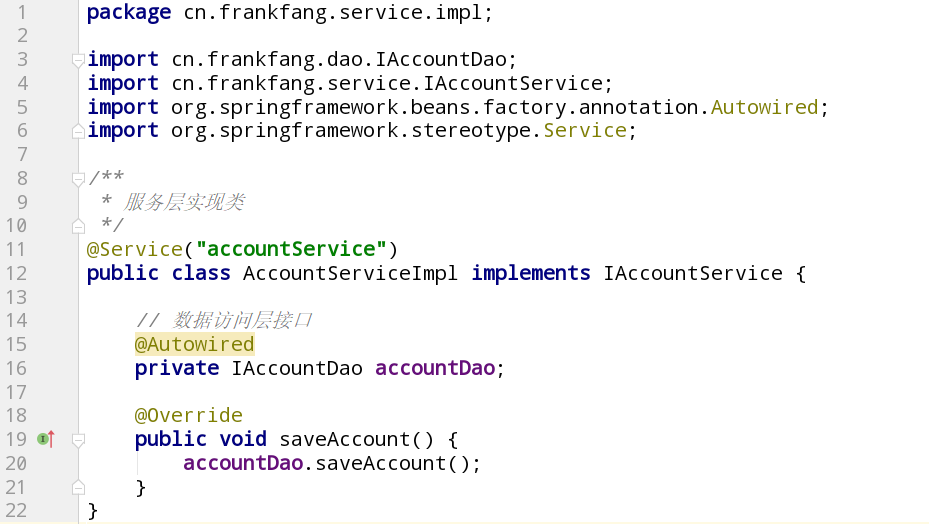
(4)服务层接口实现类AccountServiceImpl
1 | package cn.frankfang.service.impl; |
2、导入依赖
在项目的pom.xml文件中添加以下内容:
1 | <dependencies> |
这里我使用的版本是5.2.2.RELEASE,请根据需要自行导入相应的版本。更多版本的信息请访问:spring-framework-releases或repo.spring.io 进行查询。
二、配置Spring IoC容器
1、配置元数据
在项目的resources路径下新建一个spring-config.xml配置文件,并添加以下内容:
1 |
|
<bean>标签:用于配置让Spring创建对象,并存入IoC容器中,默认情况下调用的是类中的无参构造方法id属性:bean对象的唯一标识class属性:指定要创建对象的全限定类名
实际上,仅仅配置这些内容是不足以实现功能的,不过我们现在的目的仅仅是测试Spring框架是否能正常的工作,完整的配置稍后将详细地进行介绍。
2、初始化容器
在编写完配置文件之后需要将容器进行初始化,初始化的方法也非常的简单,在主方法中添加以下代码即可:
1 | ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); |
ApplicationContext接口的实现类常用的有三种,下面给出这三种实现类的相关内容:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类的根路径下加载配置文件FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从磁盘路径下加载配置文件,可读取任意位置的配置文件AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:当使用注解方式配置Spring容器时使用该实现类
注:当使用XML配置Spring容器时,推荐使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来加载配置文件,若需获取更多关于Spring加载资源的信息,请参阅:Application Contexts and Resource Paths。
3、使用容器
当初始化容器之后就可以使用容器了,下面是示例代码:
1 | package cn.frankfang; |
运行程序,在控制台打印出accountService对象的信息,表明已经成功地创建了Spring容器并可以从中取出bean对象。
以上就是创建并使用Spring容器的完整流程,下面将对其中的一些内容进行详细介绍。
三、bean标签
在上文中已经使用了bean标签来配置服务层和数据访问层对象,下面将详细介绍bean标签的相关内容。
1、属性(Attribute)
bean标签包含id、class、scope、init-method、destroy-method等属性,下面将通过表格对这些属性进行介绍:
| 属性名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
id |
给对象在容器中提供一个唯一的标识,用于获取对象 |
class |
指定类的全限定类名,用于创建对象 |
scope |
指定对象的作用范围,关于作用范围将在下文进行详细介绍 |
init-method |
指定类中的初始化方法名称 |
destroy-method |
指定类中销毁方法名称 |
除了上述属性之外,bean标签还包括name、factory-bean、factory-method等属性。若需获取更多关于bean标签属性的内容,请参阅:Bean Overview。
2、作用域(Scope)
Spring框架支持六个作用域,其中四个仅在使用web感知(web-aware)的ApplicationContext时可用。也可以创建自定义作用域。下面将通过表格说明Spring容器中bean的作用域:
| 作用域 | 说明 |
|---|---|
singleton |
将单个bean定义限定为单个实例(默认) |
prototype |
将单个bean定义的范围限定为任意数量的对象实例(多例) |
request |
将单个bean定义限定为单个HTTP请求的生命周期(仅适用于Web应用) |
session |
将单个bean定义限定到HTTP会话的生命周期(仅适用于Web应用) |
application |
将单个bean定义限定为ServletContext的生命周期(仅适用于Web应用) |
websocket |
将单个bean定义限定到WebSocket的生命周期(仅适用于Web应用) |
若需获取更多关于bean作用域的内容,请参阅:Bean Scope。
3、生命周期(Lifecycle)
bean的生命周期主要包括初始化、使用和销毁阶段。下面将介绍作用域为singleton和prototype的bean实例的生命周期:
(1)作用域为singleton:
- 初始化阶段:当应用加载创建容器时对象即被创建
- 使用阶段:只要容器存在,对象便一直存活
- 销毁阶段:当应用停止销毁容器时对象即被销毁
(2)作用域为prototype:
- 初始化阶段:当使用对象时才会创建新的实例
- 使用阶段:只要容器存在,对象便一直存活
- 销毁阶段:当对象长时间不被使用时被JVM垃圾回收器回收
若需获取更多关于bean生命周期的内容,请参阅:Lifecycle Callbacks。
四、依赖注入
依赖注入(Dependency Injection)是一个过程,对象仅通过构造函数参数、工厂方法的参数或在对象实例构造或从工厂方法返回后在对象实例上设置的属性来定义它们的依赖项(即与它们一起工作的其他对象)。然后容器在创建bean时注入这些依赖项。这个过程基本上是bean本身的逆过程(因此称为控制反转),通过使用类的直接构造或服务定位器模式来控制其依赖项的实例化或位置。
使用DI原则,代码更干净,当对象具有依赖关系时,解耦更有效。对象不查找其依赖项,也不知道依赖项的位置或类。因此,类变得更容易测试,特别是当依赖关系在接口或抽象基类上时,这些接口或抽象基类允许在单元测试中使用存根或模拟实现。
依赖注入主要可通过两种方式实现,下面将分别介绍这两种方法:
1、通过构造方法注入(Constructor-based)
该方法通过使用类中的构造方法给成员变量进行赋值,而赋值的操作是通过配置让Spring容器来进行注入。下面将对上面的项目代码进行改造,以实现通过构造方法进行注入。
(1)服务层实现类AccountServiceImpl
1 | package cn.frankfang.service.impl; |
(2)spring-config.xml配置文件
1 |
|
可以看到,通过配置<constructor-arg>标签的相关属性即可实现依赖注入,下面对该标签的所有属性进行详细介绍:
| 属性 | 功能 |
|---|---|
index |
指定参数在构造方法参数列表的索引位置 |
type |
指定参数在构造方法中的数据类型 |
name |
指定参数在构造方法中的名称 |
value |
支持注入基本数据类型和java.lang.String类型 |
ref |
支持注入其它bean,即在配置文件中配置过的bean |
若需获取更多关于<constructor-arg>标签的属性的用法,请参阅:Constructor-based Dependency Injection。
(3)Application类
1 | package cn.frankfang; |
因为已经实现了依赖注入,此时我们便可正常调用方法。当运行程序时,数据访问层的实现类会在控制台打印出正确的结果。
2、通过setter方法注入(Setter-based)
除了可以通过构造方法进行依赖注入之外,还可以通过setter方法进行依赖注入。该方法需要在类中提供需要注入的成员的setter方法,这样Spring框架便可通过setter方法进行依赖注入。下面将对上面的项目代码进行改造,以实现通过setter方法进行注入。
(1)服务层实现类AccountServiceImpl
1 | package cn.frankfang.service.impl; |
(2)spring-config.xml配置文件
1 |
|
通过<property>标签同样可以实现依赖注入,下面将对该标签的所有属性进行详细介绍:
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
name |
需要注入的成员变量名 |
value |
支持注入基本数据类型和java.lang.String类型 |
ref |
支持注入其它bean,即在配置文件中配置过的bean |
若需获取更多关于通过setter方法实现依赖注入的细节,请参阅:Setter-based Dependency Injection。
Application类的内容与采用基于构造方法实现依赖注入相同,这里不再赘述。
注:在实际项目中,如果某个依赖是强依赖关系,推荐使用构造方法进行依赖注入;如果某个依赖是可选依赖关系,推荐使用setter方法进行依赖注入。
3、依赖注入的相关细节
下面将介绍一些依赖注入相关的细节问题:
(1)使用 p 名称空间注入数据
该方法通过在XML配置文件中导入 p 名称空间并使用p:propertyName来注入数据,它本质上还是调用类中的setter方法实现注入功能。
关于这部分的详细内容请参阅:p-namespace。
(2)注入集合类型数据
Spring框架支持注入集合类型的数据,下面将通过一个例子来说明如何使用Spring框架注入集合类型的数据:
假设AccountServiceImpl包含数组类型、List类型、Set类型、 Map类型、和Properties类型的数据,具体如下:
1 | package cn.frankfang.service.impl; |
接下来在spring-config.xml配置文件中添加以下内容:
1 | <!-- 配置Service --> |
注:如果集合存入的是引用类型,则可将<value></value>标签换成<ref bean="" />即可。
若需获取更多关于集合类型数据注入相关内容,请参阅:Dependencies and Configuration in Detail - Collections。