在之前的几篇文章中我们介绍了Spring框架中的IoC容器,这是Spring框架的核心之一。接下来我们将要介绍Spring框架中另一个核心内容——AOP,本文将介绍什么是AOP、AOP的作用以及Spring框架中AOP的理论内容。
一、AOP概述
1、什么是AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程)是通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
2、AOP的作用和优势
作用:在程序运行期间,不修改代码就可对已有方法进行增强。
AOP有以下几个方面的优势:
3、AOP的实现方式
可使用Java中的动态代理技术实现AOP。
二、AOP的具体应用
下面将通过一个具体案例来说明AOP的具体实现方法。
1、案例描述
假设有一个账户管理系统,该系统可实现对账户的增删改查功能。该系统分为服务层和数据访问层,使用c3p0作为数据库连接池,使用Commons DbUtils作为操作数据库的工具类,项目的部分代码如下:
实体类Account
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package cn.frankfang.pojo;
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Double money;
}
|
服务层接口IAccountService
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package cn.frankfang.service;
import cn.frankfang.pojo.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface IAccountService {
boolean saveAccount(Account account);
Account findById(Integer id);
List<Account> getAll();
boolean updateAccount(Account account);
boolean deleteAccount(Integer id);
}
|
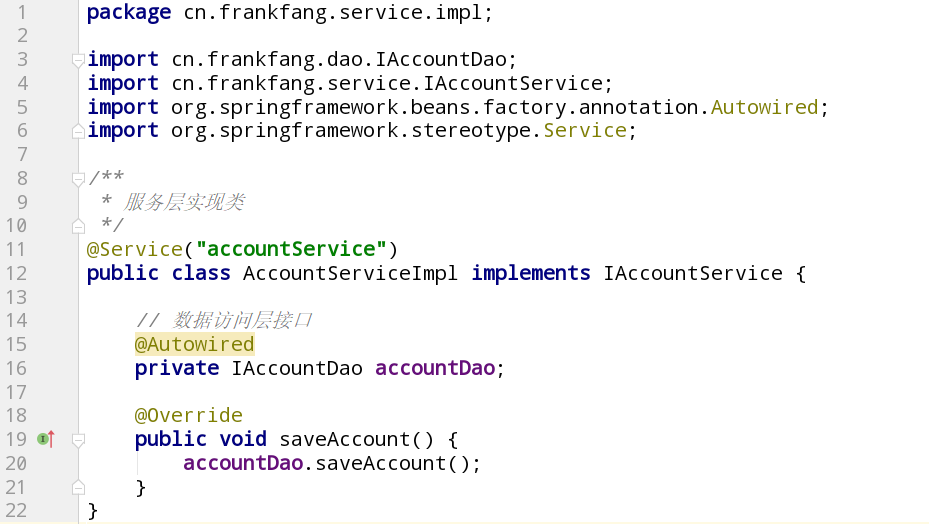
服务层实现类AccountServiceImpl
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| package cn.frankfang.service.impl;
import cn.frankfang.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.frankfang.pojo.Account;
import cn.frankfang.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public boolean saveAccount(Account account) {
return accountDao.saveAccount(account) > 0;
}
@Override
public Account findById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.selectById(id);
}
@Override
public List<Account> getAll() {
return accountDao.getAll();
}
@Override
public boolean updateAccount(Account account) {
return accountDao.updateAccount(account) > 0;
}
@Override
public boolean deleteAccount(Integer id) {
return accountDao.deleteAccount(id) > 0;
}
}
|
数据访问层接口IAccountDao
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package cn.frankfang.dao;
import cn.frankfang.pojo.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface IAccountDao {
int saveAccount(Account account);
Account selectById(Integer id);
List<Account> getAll();
int updateAccount(Account account);
int deleteAccount(Integer id);
}
|
数据访问层实现类AccountDaoImpl
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| package cn.frankfang.dao.impl;
import cn.frankfang.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.frankfang.pojo.Account;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Resource
private QueryRunner runner;
@Override
public int saveAccount(Account account) {
try{
return runner.update("insert into account(id,name,money)values(?,?,?)",
account.getId(),
account.getName(),
account.getMoney());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public Account selectById(Integer id) {
try {
return runner.query("select * from account where id = ? ",
new BeanHandler<>(Account.class), id);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public List<Account> getAll() {
try{
return runner.query("select * from account",
new BeanListHandler<>(Account.class));
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public int updateAccount(Account account) {
try{
return runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",
account.getName(),
account.getMoney(),
account.getId());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public int deleteAccount(Integer id) {
try{
return runner.update("delete from account where id=?", id);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
Spring的配置类SpringConfiguration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| package cn.frankfang.config;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("cn.frankfang")
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class SpringConfiguration {
@Value("${database.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${database.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${database.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${database.password}")
private String password;
@Bean("dataSource")
public DataSource dataSource () {
try {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass(driver);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);
dataSource.setUser(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Bean("runner")
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner queryRunner (@Qualifier("dataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new QueryRunner(dataSource);
}
}
|
配置文件application.properties
1
2
3
4
| database.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
database.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useAffectedRows=true
database.username=root
database.password=123456
|
上面的业务代码其实是存在一定问题的,问题就是业务层无法控制数据库的事务。由于上面每个方法只执行了一条SQL语句,就算无法在业务层控制事务问题也不大。但如果某一个业务一次需要执行多条SQL语句,这时就存在一定的问题了。
如果我们需要添加一个转账的功能,实现该功能的代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| @Override
public boolean transfer(Integer sourceAccountId, Integer targetAccountId, Double money) {
Account sourceAccount = accountDao.selectById(sourceAccountId);
Account targetAccount = accountDao.selectById(targetAccountId);
if (sourceAccount.getMoney() < money) {
return false;
}
sourceAccount.setMoney(sourceAccount.getMoney() - money);
targetAccount.setMoney(targetAccount.getMoney() + money);
if (accountDao.updateAccount(sourceAccount) == 0) {
return false;
}
int i = 1 / 0;
if (accountDao.updateAccount(targetAccount) == 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
|
可以看到,实现该功能需要执行多条SQL语句。如果在两次将修改后的余额写入数据库之间出现了异常(在代码中模拟了一个异常),就会导致写入数据库的数据是不完整的,即破坏了事务的一致性。那么又该怎么去解决这个问题呢?
2、案例分析
要想解决这个问题,就需要让业务层来控制事务的提交和回滚,而默认情况下每次执行SQL都是一次不同的事务,因此我们需要将连接和当前线程进行绑定,所以需要写一个连接的工具类用于从数据源中获取一个连接并实现和线程的绑定。
除此之外,还需要编写一个事务管理的工具类,需要提供开启事务、提交事务、回滚事务和释放连接的方法。
3、通过传统方法实现
(1)连接工具类ConnectionUtils
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| package cn.frankfang.utils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
@Component("connectionUtils")
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal<>();
private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public Connection getThreadConnection() {
try{
Connection conn = tl.get();
if (conn == null) {
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
tl.set(conn);
}
return conn;
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void removeConnection(){
tl.remove();
}
}
|
(2)事务管理工具类TransactionManager
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| package cn.frankfang.utils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("transactionManager")
public class TransactionManager {
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
@Autowired
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
public void beginTransaction(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void commit(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void rollback(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void release(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();
connectionUtils.removeConnection();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
(3)SpringConfiguration配置类和AccountDaoImpl实现类
首先对配置类做以下修改:
1
2
3
4
5
| @Bean("runner")
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner queryRunner () {
return new QueryRunner();
}
|
这样改的目的是为了让QueryRunner从ConnectionUtils工具类中获取数据源。所以接下来要在数据访问层的实现类AccountDaoImpl修改以下内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| package cn.frankfang.dao.impl;
import cn.frankfang.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.frankfang.pojo.Account;
import cn.frankfang.utils.ConnectionUtils;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private QueryRunner runner;
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
@Autowired
public void setRunner(QueryRunner runner) {
this.runner = runner;
}
@Autowired
public AccountDaoImpl(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
@Override
public int saveAccount(Account account) {
try{
return runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),
"insert into account(id,name,money)values(?,?,?)",
account.getId(),
account.getName(),
account.getMoney());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public Account selectById(Integer id) {
try {
return runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),
"select * from account where id = ? ",
new BeanHandler<>(Account.class), id);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public List<Account> getAll() {
try{
return runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),
"select * from account",
new BeanListHandler<>(Account.class));
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public int updateAccount(Account account) {
try{
return runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),
"update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",
account.getName(),
account.getMoney(),
account.getId());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public int deleteAccount(Integer id) {
try{
return runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),
"delete from account where id=?", id);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
(4)服务层实现类AccountServiceImpl
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
| package cn.frankfang.service.impl;
import cn.frankfang.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.frankfang.pojo.Account;
import cn.frankfang.service.IAccountService;
import cn.frankfang.utils.TransactionManager;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao accountDao;
private TransactionManager transactionManager;
@Autowired
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Autowired
public void setTransactionManager(TransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
}
@Override
public boolean saveAccount(Account account) {
try {
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
boolean result = accountDao.saveAccount(account) > 0;
transactionManager.commit();
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
transactionManager.release();
}
}
@Override
public Account findById(Integer id) {
try {
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
Account account = accountDao.selectById(id);
transactionManager.commit();
return account;
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
transactionManager.release();
}
}
@Override
public List<Account> getAll() {
try {
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
List<Account> list = accountDao.getAll();
transactionManager.commit();
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
transactionManager.release();
}
}
@Override
public boolean updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
boolean result = accountDao.updateAccount(account) > 0;
transactionManager.commit();
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
transactionManager.release();
}
}
@Override
public boolean deleteAccount(Integer id) {
try {
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
boolean result = accountDao.deleteAccount(id) > 0;
transactionManager.commit();
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
transactionManager.release();
}
}
@Override
public boolean transfer(Integer sourceAccountId, Integer targetAccountId, Double money) {
try {
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
Account sourceAccount = accountDao.selectById(sourceAccountId);
Account targetAccount = accountDao.selectById(targetAccountId);
if (sourceAccount.getMoney() < money) {
return false;
}
sourceAccount.setMoney(sourceAccount.getMoney() - money);
targetAccount.setMoney(targetAccount.getMoney() + money);
accountDao.updateAccount(sourceAccount);
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.updateAccount(targetAccount);
transactionManager.commit();
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
transactionManager.release();
}
}
}
|
可以看到,我们在每个方法中都加入了事务控制,这样就达到了在业务层控制事务的目的,运行程序,当出现异常时事务就会回滚,通过查询数据库可以发现数据并未被修改,这就代表上面的代码成功的实现了功能。
4、通过动态代理实现
虽然上面的方法确实可以实现功能,但写起来非常繁琐。此外,如果对事务管理的类进行修改的话,所有开始事务控制的方法都要进行修改,换句话说就是上面的代码耦合度太高了。那么有什么办法可以降低程序的耦合度吗?答案就是使用Java中的动态代理技术来降低程序的耦合度并实现相同的功能。
我们使用JDK自带的Proxy类对IAccountService接口进行代理,所以在SpringConfiguration配置类中添加以下内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| @Bean("accountService")
public IAccountService accountService (@Qualifier("accountDao") AccountDaoImpl accountDao,
@Qualifier("transactionManager") TransactionManager transactionManager) {
final IAccountService accountService = new AccountServiceImpl(accountDao);
IAccountService proxyAccountService = (IAccountService) Proxy
.newProxyInstance(accountService.getClass().getClassLoader(),
accountService.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
result = method.invoke(accountService, args);
transactionManager.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
transactionManager.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
transactionManager.release();
}
return result;
}
});
return proxyAccountService;
}
|
而AccountServiceImpl则改下为如下形式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
| package cn.frankfang.service.impl;
import cn.frankfang.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.frankfang.pojo.Account;
import cn.frankfang.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public AccountServiceImpl(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public boolean saveAccount(Account account) {
return accountDao.saveAccount(account) > 0;
}
@Override
public Account findById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.selectById(id);
}
@Override
public List<Account> getAll() {
return accountDao.getAll();
}
@Override
public boolean updateAccount(Account account) {
return accountDao.updateAccount(account) > 0;
}
@Override
public boolean deleteAccount(Integer id) {
return accountDao.deleteAccount(id) > 0;
}
@Override
public boolean transfer(Integer sourceAccountId, Integer targetAccountId, Double money) {
Account sourceAccount = accountDao.selectById(sourceAccountId);
Account targetAccount = accountDao.selectById(targetAccountId);
if (sourceAccount.getMoney() < money) {
return false;
}
sourceAccount.setMoney(sourceAccount.getMoney() - money);
targetAccount.setMoney(targetAccount.getMoney() + money);
if (accountDao.updateAccount(sourceAccount) == 0) {
return false;
}
int i = 1 / 0;
if (accountDao.updateAccount(targetAccount) == 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
|
运行程序,当出现异常时事务就会回滚,通过查询数据库可以发现数据并未被修改,这就代表上面的代码成功的实现了功能。
可以看到,相对于传统的方法进行事务控制,动态代理可以实现在不改变原有实现类的情况下对实现类进行增强,降低了程序的耦合度,使代码的维护升级更加容易,这就是AOP的好处。Spring框架中的AOP也是由动态代理来实现的,下面我们将介绍Spring框架中的AOP。
三、Spring中的AOP
Spring框架通过使用基于XML配置文件的方法或@AspectJ注释形式提供了编写自定义切面的简单而强大的方法。接下来我们将介绍与Spring AOP相关的概念。
1、相关术语
下面将列出Spring AOP的相关术语:
Aspect:切面。是切入点和通知(引介)的结合Join point:连接点。是指那些被拦截到的点,在Spring中这些点指的是方法(Spring只支持方法类型的连接点)Advice:通知/增强。是指拦截到连接点之后要做的事情Pointcut:切入点。是指我们要对哪些连接点进行拦截的定义Introduction:引介。这是一种特殊的通知,可以在不修改类代码的前提下在运行期动态地对类添加一些方法或成员变量Target object:目标对象。是指代理的目标对象AOP proxy:代理。是指一个类被AOP织入增强后就产生一个结果代理类Weaving:织入。是指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程
2、功能和目标
- Spring AOP是用纯Java实现的。不需要特殊的编译过程。Spring AOP不需要控制类加载器层次结构,因此适合在servlet容器或应用服务器中使用。
- Spring AOP目前只支持方法执行连接点(建议在Spring Bean上执行方法)。虽然可以在不破坏核心Spring AOP APIs的情况下添加对字段截取的支持,但是没有实现字段截取。如果需要建议字段访问和更新连接点,请考虑使用AspectJ之类的语言。
- Spring AOP的AOP方法不同于大多数其他AOP框架。其目的并不是提供最完整的AOP实现(尽管Spring AOP非常有能力)。相反,其目的是在AOP实现和Spring IoC之间提供紧密的集成,以帮助解决企业应用程序中的常见问题。
- Spring框架的AOP功能通常与Spring IoC容器一起使用。方面是通过使用普通
bean定义语法配置的(尽管这允许强大的“自动代理”功能)。这是与其他AOP实现的一个关键区别。使用Spring AOP不能轻松或高效地完成某些事情,例如建议非常细粒度的对象(通常是域对象)。在这种情况下,AspectJ是最佳选择。
若需获取更多关于Spring AOP的理论内容,请参阅:Aspect Oriented Programming with Spring。